Inderpreet Singh writes on the Hackaday blog about Henner Zeller’s latest project:

Laser PCBs with LDGraphy
There are many, many ways to get a PCB design onto a board for etching. Even with practice however, the quality of the result varies with the process and equipment used. With QFN parts becoming the norm, the days of etch-resist transfers and a permanent marker are all but gone. Luckily, new and improved methods of Gerber transfer have be devised in recent years thanks to hackers across the world.
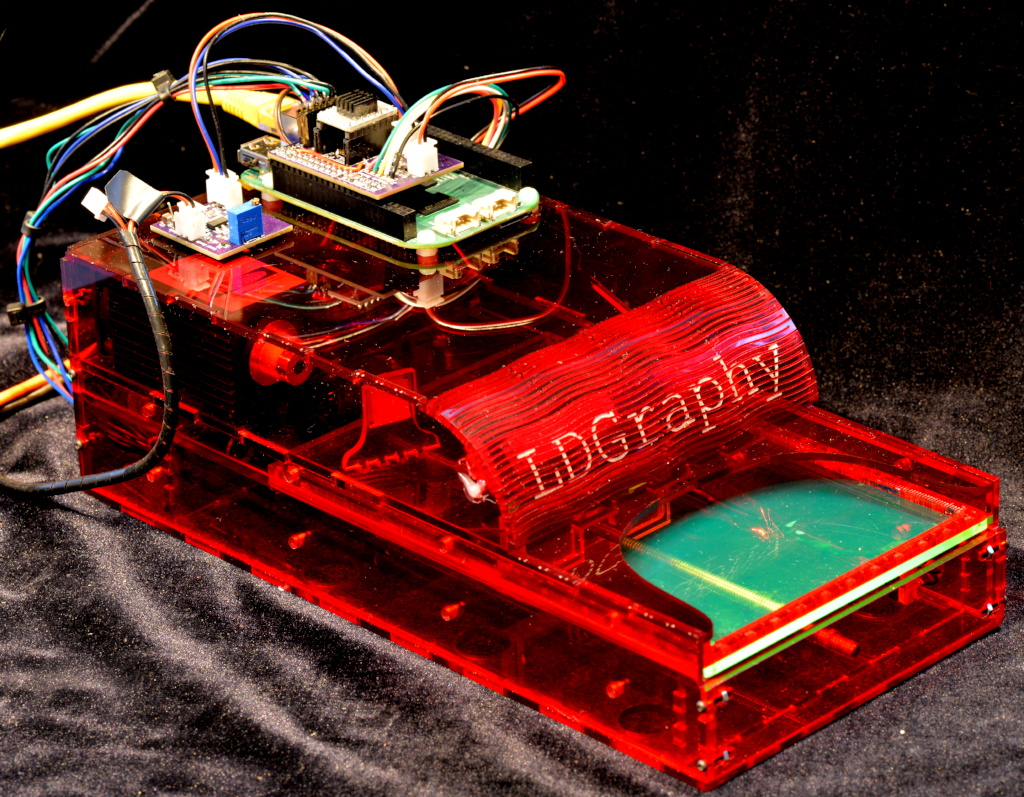
One such hacker, [Henner] is working on a project called LDGraphy in an attempt to bring high-resolution etching to the masses. LDGraphy is a laser lithography device that makes use of a laser and a Beaglebone green to etch the layout onto the board. The best part is that the entire BOM is claimed to cost under a $100 which makes it affordable to people on a budget.
The system is designed around a 500 mW laser and a polygon mirror scanner meant for a laser printer. The board with photoresist is linearly actuated in the X-axis using a stepper motor and the laser beam which is bounced off the rotating hexagonal mirror is responsible for the Y-axis. The time critical code for the Programmable Realtime Unit (PRU) of the AM335X processor is written in assembly for the fast laser switching. The enclosure is, naturally, a laser cut acrylic case and is made at [Henner]’s local hackerspace.

Visit the GitHub repo for more information:
LDgraphy – Laser Direct Lithography
Simple implementation of photo resist exposure using a 405nm laser. Goal is to have this Open Source/Open Hardware system easy to reproduce with commonly available parts.

The BOM is in the order of $100 including the Beaglebone Green:
- 500mW 405nm laser ($30ish)
- Commonly available polygon mirror scanner (from laser printers) ($20ish)
- Beaglebone Black/Green to control it all (using the PRU to generate precise timings for motors and laser) ($40ish)
- Stepper motor for linear axis (plus end-stop switches) (scrap box)
- Photo diode to determine start-of-line (as the polygon mirrors have slightly different long faces and also phase-drift over time) (SFH203P)
- Local electronics: fast Laser diode driver and stepmotor driver (few $$)